Packet Generator User Guide V0.4
Based on DeanSys Pktgen-0.0.8

dean@deansys.com
www.deansys.com, Feb.20,2007
Contents
Chapter 3. Command description
Chapter 4. Global Mode Commands
4.13.2 Show Interface Command:
4.13.5 Show Packet Counter Command:
Chapter 5. Build Mode Commands
Chapter 6. Configuration Mode Commands
Chapter 1. Abstract
DeanSys Pktgen is designed by www.deansys.com. This site is Dean¡¯s personal site to design different system solutions for the different requirement. We are looking for guys who are interested in Linux/UNIX system design. Please send us email if you want to share your good ideas with us!
User Interface (UI) of this packet generator is designed following the format of switch. User can type in commands in the same way what they are doing on the switch. They can type ¡®?¡¯ anywhere to get help about the commands, can type ¡®tab¡¯ to complete the command automatically. And it offers auto-building functions that they can build well known protocol packets with some parameters automatically. User also can set the raw packets with different configuration file with a simple command.
It can only work under UNIX/Linux system. Red Hat Linux 9.0 is the best choice. And Red Hat Linux ES/AS version is also acceptable. Make sure that you have got one Ethernet interface card at least.
V0.0.4 is the first shared version. It support Command Line Interface (CLI) for the user. User can build a packet from raw text file or with the help from Protocol Builder function.
Multi users can use this packets generator at the same time. And the multi-stream and multi-task function has been supported since version 0.0.5. You can create more streams and control them at the same time. It is available to send different streams through different net interface cards at the same time. It depends on you!
Version0.0.6 has offered user an easy way to load packets from Libpcap data file. What you need is just to capture packets into Libpcap file. More function will be available in the next version.
Increased stream/packet is supported since V0.0.7. User can set some byte to be increased with the step value. When the step value is less than zero, it means decreased.
V0.0.8 is able to build ICMP echo request/reply packet for users. Fix the packet length bug. SNMP function is the new added part. It now support SNMP set/get function on SNMP V1 and V2. More SNMP/ICMP functions would be added in the future. Specially thank Thirumalesh Thirumala from cisco.com for his great proposal for icmp echo function.
The current version is v0.0.8.
The development is going on and more details will be available in the next version. Please send mail to me if you have found any bug or have got any suggestion to me. Thank you!
Copyright is an old topic. Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this document, but changing it is not allowed.
Following are some symbol logo for the reader.
|
|
This is a tip. Maybe is it useless for you. |
|
|
This is a warning. |
1.1 Scope
This document is designed for the user of packet generator or anyone who is interested with the packet generator. I am sorry that I did not spend enough time finding the mistakes in this document. Then please send me mail if you have found any mistakes in this document. Thank you!
The reader must have some basic knowledge of Ethernet packets and network.
1.2 Feature List
The packet generator is designed to support:
A. A command line interface to type in commands
B. A command generator to make commands easy to type
C. Command history to record your commands
D. Build well-known protocol packets with the building command.
E. Read raw text file to build any packet.
F. Load packet data from Libpcap data file.
G. SNMP
H. Multi-task and multi-stream to send packets at the same time.
I. System logging.
J. Increased/Decreased streams.
K. Others.
New feature will be added in the coming versions.
Chapter 2. How to install it?
Get the tar ball and use the following command to install it:

Then it is available for you.
Make sure that the tar ball contains two files at least:
pktgen -- the main binary file
packet.conf -- the default text data file
![]() The way to build a packet looks like below:
The way to build a packet looks like below:
(1). Make sure what you want, and then start the program.
(2). Create stream you want. You can create them with:
A. Read raw packet from named text file.
B. Load packets from libpcap data file.
B. Well-known protocols with the packet building function.
(3). Set the interface name, number of packet, pause time between packets and increased mode. Or just skip them to keep the default.
(4). Check the settings of streams. Modify the setting and values if necessary. Make sure they are what you want.
(5). Send the stream you want to send.
(6). Check the result.
The first and second steps can be exchanged with each other. You decide the order.
![]() Note: You must be able to access the
interface! ¡®root¡¯ is the suggested user group.
Note: You must be able to access the
interface! ¡®root¡¯ is the suggested user group.
![]() How to change the binary¡¯s user mode and
privilege?
How to change the binary¡¯s user mode and
privilege?
Just type following commands:
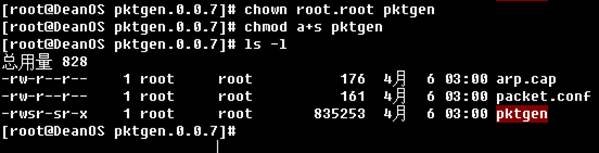
Chapter 3. Command description
There are three command modes in the packet generator. They are global mode, configuration mode and build mode.
Global mode contains the basic commands of this packet generator. You can check the stream, edit the packet buffer or stream, and send packets. They are the basic level commands.
Build mode is used to build packets. You can build it with protocol building function, reading raw text and loading libpcap data file.
Configuration mode is used to modify different settings with a specified stream.
All the commands can be listed by typing ¡®?¡¯ or help. And all the commands can be completed automatically by type ¡®tab¡¯. Short and uncompleted commands are also available.
Colors will be used to make the messages more easy-reading.
Error and warning messages will be printed with red color.
Status and help messages will use green or yellow.
Chapter 4. Global Mode Commands
Run the program and you will be into the global mode:
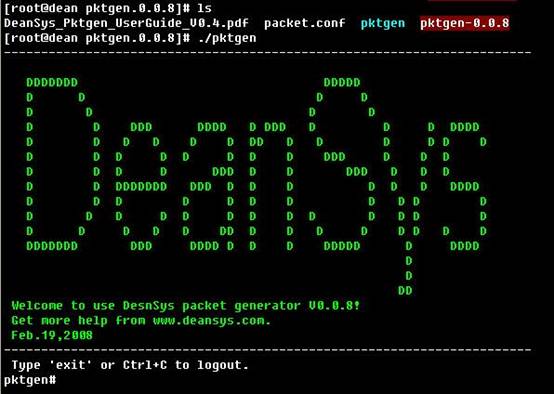
Type ¡®?¡¯ to get the command list as :
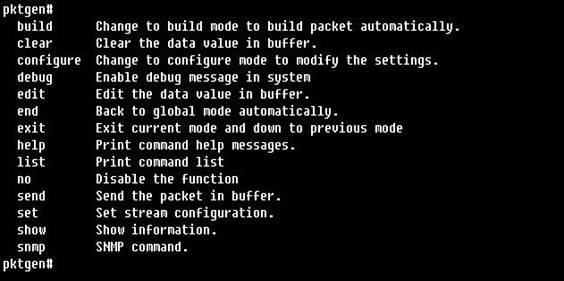
Type ¡®list¡¯ to get command list:

4.1 Build Command:
Type ¡®build¡¯ to enable build mode. Then packet builder function is available for you. This command has an optional parameter: [Stream ID]. You can specify the stream ID number which you want to build or just keep it empty to use the default stream ID 1 with the default packet configuration file.
If the stream you specify is not existed, system will help you to create a default stream name stream 1 with default setting and values.
pktgen#build
Select packet.conf as the default config file.
Create new stream :1 with default configuration.
Change to build mode!
pktgen(build)#
pktgen#build 2
Select packet.conf as the default config file.
Create new stream :2 with default configuration.
Change to build mode!
pktgen(build)#
4.2 Clear Command:
This command is used to reset the value in buffer to zero. You can specify the stream ID number which to be cleared. Stream ID is an optional parameter
pktgen#clear
Debug : Clear the buffer of stream 1.
pktgen#
pktgen#clear 2
Debug : Clear the buffer of stream 2.
pktgen#
4.3 Configure Command:
Type in ¡®configure¡¯ to enable configuration mode. Then you can modify the stream setting such as: interface, number, length and pause time. You can specify the stream ID number which to be configured. Stream ID is an optional parameter.
![]() If the stream you specify is not
existed, system will help you to create a default stream name stream 1 with
default setting and values.
If the stream you specify is not
existed, system will help you to create a default stream name stream 1 with
default setting and values.
pktgen#configure
Change to Stream :1
Change to configure mode!
pktgen(config)#
pktgen#configure 2
Select packet.conf as the default config file.
Create new stream :2 with default configuration.
Change to configure mode!
pktgen(config)#
4.4 Debug Command:
Command of ¡®debug¡¯ is used to enable the system logging function. After you have enabled this function, system will print much more logging messages. You can use ¡®no debug¡¯ to disable it.
4.5 Edit Command:
Type ¡®edit <1-1518> VALUE [StreamID]¡¯ to modify the value in stream buffer. You can use ¡®show¡¯ first to verify the value in buffer. The packet units is from 1 to 1518.
You can specify the stream ID number which to be configured. Stream ID is an optional parameter
pktgen#show buffer
Packet Generator Status:
Device: eth0, Length: 64 byte, Number: 1, Pause: 0 s
Data from Configuration file.
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
----+----------------------- -----------------------
0001|ff ff ff ff ff ff 01 02 03 04 05 06 88 8e 01 01
0002|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0003|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0004|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0005|
----+----------------------- -----------------------
pktgen#edit
<1-1518> Position in buffer.
pktgen#edit 1
VALUE The value you want to set.( 0x0-0xFF)
pktgen#edit 1 0
<cr>
<1-16> Stream ID number.Default is the last stream.
pktgen#edit 1 0 1
<cr>
pktgen#edit 1 0 1
pktgen#
![]() The first byte in buffer here is 1, not 0.
It is just to be easy to read. Both of decimal and hex value is acceptable.
(Hex value is beginning with 0x)
The first byte in buffer here is 1, not 0.
It is just to be easy to read. Both of decimal and hex value is acceptable.
(Hex value is beginning with 0x)
4.6 End Command:
Command of ¡®end¡¯ is used to go back to global mode from anywhere.
4.7 Exit Command:
Command of ¡®exit¡¯ is used to end the execution and exit the system.
4.8 Help Command:
Command of ¡®help¡¯ is used to show the help message about the system and commands.
4.9 List Command:
Command of ¡®list¡¯ is used to list all the command in current mode.
4.10 No Command:
Command of ¡®no¡¯ is used to disable some function or delete some settings.
At now, only ¡®no debug¡¯ is supported to disable system debug function.
4.11 Set Command:
Command of ¡®set¡¯ is used to enable the increased mode on a stream. You need to specify the stream ID, position of buffer and the step value. The max step value is 65535 and max increased buffer is 2 bytes (16bits, 65536).
4.12 Send Command:
Type in ¡®send¡¯ command to send the packet in buffer with the configuration value. You can select to send a specify stream or all of them. If you just type in ¡®send¡¯, system will send the last stream you configure/build only.
System is able to send all the streams at the same time. If there are more than one stream on the same interface, system will send them at the same time with mixing them together. Stream schedule will be available in the next version. Then you can specify the transmit mode with multi-stream (one by one, or mixed together).
pktgen#send ?
<cr>
<1-16> Stream ID number.(1-16)
all All the stream.
pktgen#send
pktgen#send
Packet Number :1 Length :64 Device :eth0
Wrote 64 bytes packet; check the wire.
pktgen#
4.13 Show Command:
¡®show ¡¯ command is used to show the packet generator status. It contains streams status and system status.
pktgen#show ?
buffer Show buffer information.
interface Interface status and configuration
memory Memory allocate/free status
netstat Network status and configuration
packet Packet status and configuration
router Local router status and configuration
stream Displays the last stream status.
system Displays system status
version Displays pktgen version
pktgen#show
4.13.1 Show Buffer Command:
This command is used to check the data in buffer. The size of content depends on the length of packet.
You can specify the stream with the stream ID number. It is an optional parameter. System will print the last buffer you configure/build if there is no stream ID given.
pktgen#show buffer
Packet Generator Status:
Device: eth0, Length: 64 byte, Number: 1, Pause: 0 s
Data from Configuration file.
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
----+----------------------- -----------------------
0001|ff ff ff ff ff ff 01 02 03 04 05 06 88 8e 01 01
0002|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0003|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0004|00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
0005|
----+----------------------- -----------------------
pktgen#
4.13.2 Show Interface Command:
This command is used to show the interface status and setting. Interface name is optional.
pktgen#show interface
[WORD] Inteface name
pktgen#show interface
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:43:5F:A0
inet addr:192.168.110.98 Bcast:192.168.110.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:715985 errors:10 dropped:41 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:110995 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:69181980 (65.9 Mb) TX bytes:22037593 (21.0 Mb)
Interrupt:10 Base address:0x1080
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:43:5F:AA
BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:6 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:1671 (1.6 Kb) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
Interrupt:9 Base address:0x1400
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:179 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:179 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:21853 (21.3 Kb) TX bytes:21853 (21.3 Kb)
pktgen#
4.13.3 Show Memory Command:
This command is used to show the system memory status. The information contains physical memory, virtual memory and swap partition.
pktgen#show memory
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 194668 185056 9612 0 85460 63528
-/+ buffers/cache: 36068 158600
Swap: 425712 5096 420616
pktgen#
4.13.4 Show Netstat Command:
This command is used to show the system network session status.
pktgen#show netstat
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 *:32768 *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 DeanOS:32769 *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 *:cvspserver *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 *:sunrpc *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 DeanOS:ipp *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 DeanOS:smtp *:* LISTEN
tcp 0 20 192.168.110.98:ssh dean:1312 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.110.98:ssh dean:1305 ESTABLISHED
udp 0 0 *:32768 *:*
udp 0 0 *:906 *:*
udp 0 0 *:sunrpc *:*
udp 0 0 *:631 *:*
Active UNIX domain sockets (servers and established)
Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 78166
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 78165
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 78009
unix 3 [ ] STREAM CONNECTED 78008
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 2023
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1854
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1819
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1805
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1747
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1502
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1359
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 1324
pktgen#
4.13.5 Show Packet Counter Command:
This command is used to show the system packet counters. Interface name is optional. Default value is to show all of them.
pktgen#show packet counter
Iface MTU RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP
eth0 1500 720885 10 41 111077 0 0
eth1 1500 6 0 0 0 0 0
lo 16436 179 0 0 179 0 0
pktgen#
4.13.6 Show Router Command:
This command is used to check the system router status.
pktgen#show router
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.110.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
169.254.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
127.0.0.0 * 255.0.0.0 U 0 0 0 lo
default gateway 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
pktgen#
4.13.7 Show Stream Command:
This command is used to check the stream status. You can specify the stream ID which you want. It is an optional value. Default value is to show all of the streams.
pktgen#show stream ?
<cr>
<1-16> Stream ID numebr.
pktgen#show stream
Current Stream status:
ID Length Interface Number Pause From
------ -------- ------------ -------- -------- ----------
1 64 eth0 1 0 File
------ -------- ------------ -------- -------- ----------
Total Stream :1
pktgen#
4.13.8 Show System Command:
This command is used to check the system status.
pktgen#show system
DeanSys Packet Generator System status:
Linux DeanOS 2.4.20-8 #1 Thu Mar 13 17:54:28 EST 2003 i686 i386 GNU/Linux
pktgen#
4.13.9 Show Version Command:
This command is used to get version information.
pktgen#show version
-----------------------------------------------
Packet Generator Version Information
Name : Packet Generator 0.0.8
Author: Dean Ding
Date : Feb.19,2008
Note : Based on GNU Linux System
: www.deansys.com
-----------------------------------------------
pktgen#
Chapter 5. Build Mode Commands
Type ¡®build¡¯ to change to build mode. Then you will get the commands to build well-known protocol packets.
pktgen#build
pktgen(build)#
Type ¡®?¡¯ to get commands help message:
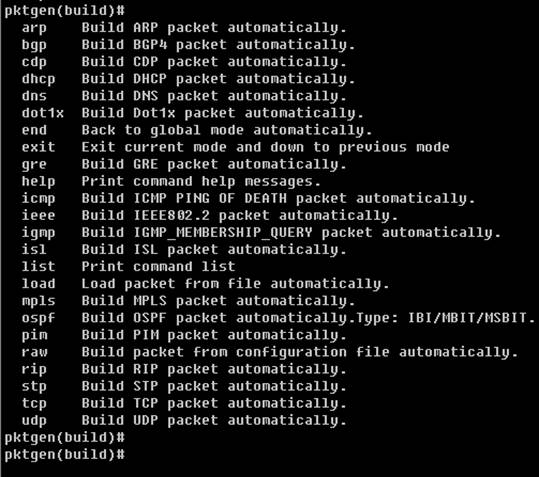
Table 2 Build mode command
|
Command |
Description |
|
arp |
Build ARP packet. |
|
bgp |
Build BGPv4 packet. (OPEN, UPDATE, NOTIFICATION, KEEPALIVE) |
|
cdp |
Build CDP packet. |
|
dhcp |
Build DHCP packet. (REQUEST, REPLY) |
|
dns |
Build DNS packet. |
|
dot1x |
Build 802.1x EAP packet. (START, LOGOFF, EAP PACKET) |
|
end |
Back to global mode. |
|
exit |
Exit to global mode. |
|
gre |
Build GRE packet. |
|
help |
Print command help message. |
|
icmp |
Build ICMP packet. |
|
ieee |
Build IEEE 802.2/802.3 packet |
|
isl |
Build ISL packet. |
|
igmp |
Build IGMP packet. (MEMBERSHIP_QUERY, MEMBERSHIP_REPORT, LEAVE_GROUP) |
|
load |
Load packets from libpcap data file |
|
list |
Print commands list. |
|
mpls |
Build MPLS packet. |
|
ospf |
Build OSPF packet. (HELLO, UMD, LSA, DBD, LSR, LSU) |
|
pim |
Build PIM packet |
|
raw |
Build raw packets with configuration file. |
|
rip |
Build RIP packet. (REQUEST, RESPONSE, TRACEON, TRACEOFF, POLL, POLLENTRY, MAX) |
|
stp |
Build STP packet. |
|
tcp |
Build TCP packet. |
|
udp |
Build UDP packet. |
|
? |
Get help message |
5.1 OSPF Commands:
Type in ¡®ospf ?¡® in build mode, then you will find the types of OSPF.
pktgen(build)#ospf ?
dbd OSPF DBD packet.
hello OSPF Hello packet.
lsa OSPF LSA packet.
pktgen(build)#
The OSPF command list is :
ospf dbd [dest_ip] [src_ip] [type]
ospf hello [dest_ip] [src_ip] [neighbor_ip]
ospf lsa [dest_ip] [src_ip]
5.1.1 OSPF DBD command:
The DBD type is : IBI/MBIT/MSBIT
pktgen(build)# ospf dbd 192.168.110.1 192.168.110.254 ibi
5.1.2 OSPF HELLO command:
An expmale is:
pktgen(build)#ospf hello 192.168.110.254 192.168.110.2 192.168.110.23
5.2 RIP Commands:
RIP command format is :
rip [rip_add] [rip_netmask] [next_hop] [dest_ip]
pktgen(build)#rip 192.168.110.98 255.255.255.0 192.168.110.9 192.168.110.254
5.3 PIM Commands:
Type pim in build mode, then you will be asked for source and destination IP address. It just support PIMv2 HELLO packet right now.
pktgen(build)# pim hello 192.167.110.1 19.168.11.1
5.4 RAW Commands:
Type in raw command in build mode to select an existed configuration file to load the packet data from. The default configuration file is ¡®packet.conf¡¯. Default will be selected if you just type raw without any parameter.
For example, if you want to use the default configuration file, then just type ¡®raw¡¯:
pktgen(build)#raw
Select packet.conf as the default config file.
If you want to use another file, just type ¡®raw filename¡¯
pktgen(build)#raw test.conf
Select test.conf as the default config file.
![]() Make sure the file you have
selected is in the same fold and it should be filled with correct format. An
example file will look like:
Make sure the file you have
selected is in the same fold and it should be filled with correct format. An
example file will look like:
loada:ffffffffffff0001 02030405888e0101
loadb:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
loadc:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
loadd:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
loade:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
loadf:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
loadg:0000000000000000 0000000000000000
At present, the max length is 112 bytes. You can use ¡®length¡¯ command in configuration mode to modify the length. The default length is 60 bytes. If you want to use lager packet, please tell me that. And I will modify it later.
5.5 IGMP Command:
An example is:
pktgen(build)#igmp 224.0.0.1 192.168.110.1
5.6 Load Command:
At right now, loading function only supports libpcap format data file. You can use following command to load packets from named libpcap data file:
pktgen(build)#load
cap Select libpcap file to load.
pktgen(build)#load cap
WORD File name you want to load.
pktgen(build)#load cap arp.cap
Success to load 2 packets from arp.cap.
Packet number is [2].
pktgen(build)#
5.7 Other Commands:
The development for other protocols has not been finished yet and will be available in the next version. Please send me mail if you have found any bugs. Thanks a lot!
Chapter 6. Configuration Mode Commands
Type the command of ¡®configure¡¯ to change to configuration mode to modify the configuration setting and values. The configuration options will be: number, length, interface and pause time. You can just skip this step to keep the default value. The default value will be:
![]() Interface
eth0
Interface
eth0
Length 60bytes
Number 1
Pause time 0 second
Commands look like:

6.1 Interface Command:
Type the command of ¡®interface¡¯ to select a Network Interface Card (NIC) to send your packet. Interface name is an optional value. Default card is ¡®eth0¡¯.
pktgen(config)#interface eth0
Device is eth0
pktgen(config)#
![]() Make sure that the name of the card is correct.
Otherwise you will get error messages. Or you can query the list of the
available interface first. Just type in ¡®show interface¡¯ in global mode.
Make sure that the name of the card is correct.
Otherwise you will get error messages. Or you can query the list of the
available interface first. Just type in ¡®show interface¡¯ in global mode.
6.2 Number Command:
Type number command to set the number of packets you want to build and send out. The range is 1 - 65535. Default value is 1.
pktgen(config)#number 10
Packet number is 10
pktgen(config)#
6.3 Length Command:
Type the command of ¡®length¡¯ to set the value of packet length. The range is 16-1518. Default value is 60.
pktgen(config)#length 64
Length is 64bytes
pktgen(config)#
6.4 Pause Command:
The ¡®pause¡¯ command is to set the pause seconds and microseconds between every two packets. Second value is from 0 to 3600. Microsecond value is from 0 to 999999. Default value is 0 (no pause).
pktgen(config)#pause ?
microsecond Microsecond based time value. Pause time value.
second Second based time value. Pause time value.
pktgen(config)#pause microsecond ?
<0-999999>
pktgen(config)#pause microsecond 100 ?
<cr>
pktgen(config)#pause microsecond 100
pktgen(config)#pause ?
microsecond Microsecond based time value. Pause time value.
second Second based time value. Pause time value.
pktgen(config)#pause second ?
<0-3600>
pktgen(config)#pause second 1
pktgen(config)#
![]() As the reason of Linux kernel, the
microsecond time value is not as exactly as we expected. Then it is recommended
not to set the microsecond value less then 100.
As the reason of Linux kernel, the
microsecond time value is not as exactly as we expected. Then it is recommended
not to set the microsecond value less then 100.
6.5 Time Command:
Type time command to set the pause seconds between every two packets. The range is 0-3600. Default value is 0 (no pause).
pktgen(config)#time 1
Pause time is 1 second.
pktgen(config)#
6.6 Other Commands:
Other commands such as ¡®list¡¯ and ¡®help¡¯ are the same will the command in global mode. More configure commands will be available in the future.
Chapter 7. Advanced Usage
It is recommended to be familiar with the commands. Most of the complex simulation will be available after you have combined some necessary simple commands. Here is a simple examples.
Example One: If we want to send 65535 different source mac addresses packets through interface eth0 and eth1 at the same time, we can type following commands:

![]() It is important to design the details first.
It is important to design the details first.
It is a good idea to run this binary with some scripts (such as Shell, TCL/Expect). It will help you to create much more complex simulation!
Chapter 8. Notes
This is an unfinished version. Extra details will be added. And if you have any suggestions or ideas, please share them with me. My mail box is:
dean@deansys.com
New version packet generator binary and document will be available for anyone at my site: http://www.deansys.com.
And any of your ideas and suggestion would be welcome anytime! Please send them to me. My mailbox is dean@deansys.com. Thanks a lot!
Chapter 9. THANKS
Thank for all the guys who share me with their ideas and suggestions.
THANKS
Thirumalesh Thirumala <tthiruma@cisco.com>

Design different system solutions for different usages.